Welcome to the Blood Sugar Balancing Act
If blood sugar management were an Olympic event, we’d all be aiming for gold. But for many, keeping glucose levels steady can feel more like a rollercoaster ride—one moment you feel great, and the next, you’re searching for a quick fix to counter dizziness and fatigue.
So, how can you keep your blood sugar levels as stable as possible?
Let’s break it down.
Step 1: Understand Your Blood Sugar Targets
Knowing your target blood sugar levels is essential for effective management. The American Diabetes Association (ADA) recommends the following ranges:
- Before meals (fasting): 80-130 mg/dL
- Two hours after eating: Below 180 mg/dL
- A1C (3-month average): Below 7.0% (or under 6.5% for those seeking tighter control)
If your numbers fluctuate, don’t panic. Blood sugar management is about consistency, patience, and making gradual, sustainable changes.
Step 2: Monitor Your Blood Sugar Regularly
Tracking your blood sugar helps you understand how your body responds to food, exercise, and stress. There are two primary methods for monitoring glucose levels:
- Traditional fingerstick tests provide quick and reliable readings, though frequent testing can be inconvenient.
- Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs), such as Dexcom, FreeStyle Libre, and Medtronic, track glucose levels around the clock and send real-time data to your phone, making it easier to identify trends and make proactive adjustments.
The more consistently you monitor, the better insights you’ll gain into your glucose patterns, allowing for smarter lifestyle choices.
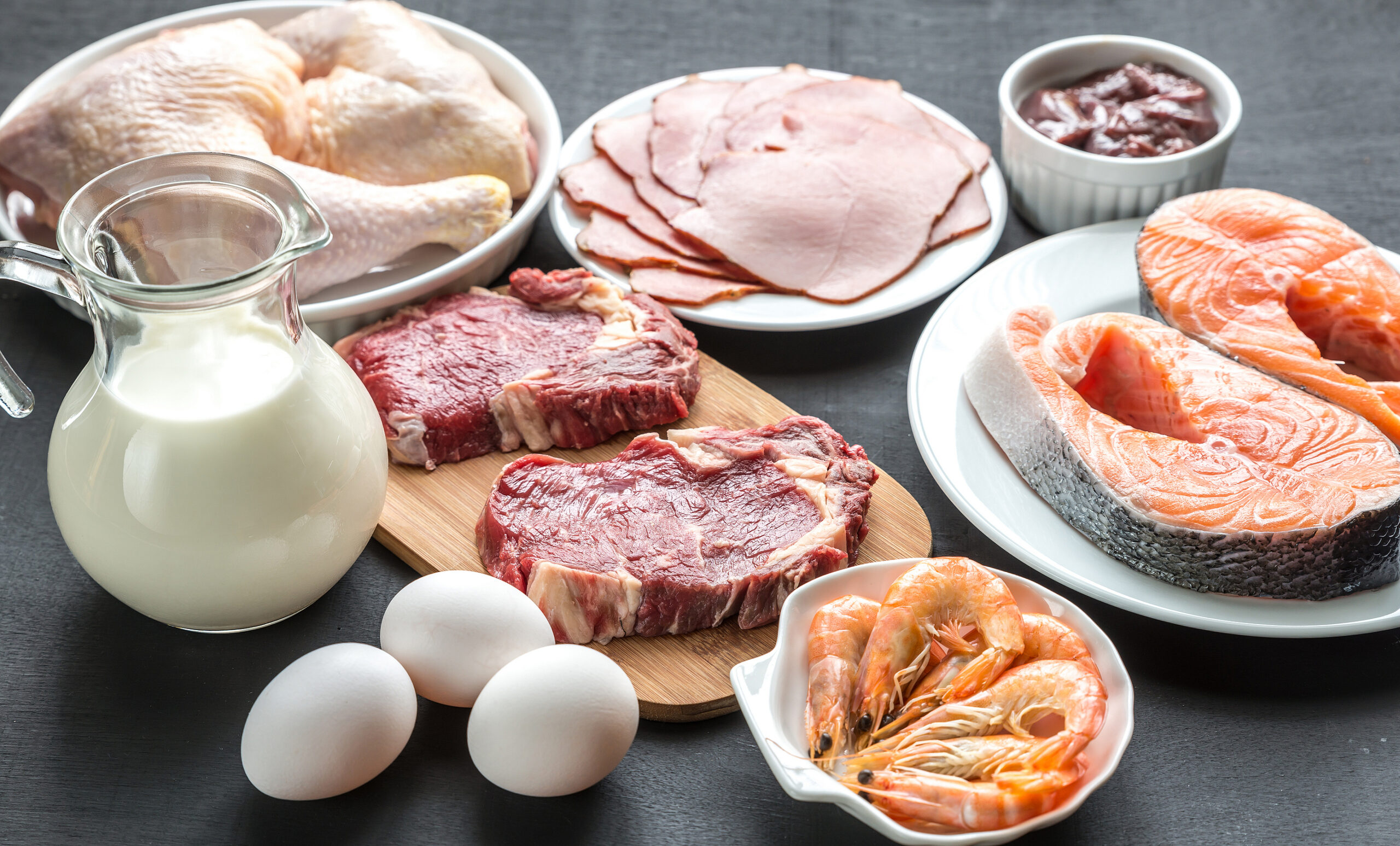

Step 3: Balance Your Diet and Exercise
Foods That Can Cause Blood Sugar Spikes
Certain foods can lead to sudden increases in blood sugar, including:
- Refined carbohydrates like white bread, white rice, and processed snacks
- Sugary beverages, such as soda, energy drinks, and flavored coffee with syrups
- Skipping meals, which can cause your body to release excess glucose and lead to spikes
Foods That Help Maintain Stable Blood Sugar
To keep blood sugar steady, focus on:
- Lean proteins, including chicken, fish, tofu, and eggs
- High-fiber foods, such as beans, lentils, and whole grains
- Non-starchy vegetables like broccoli, spinach, and bell peppers
The Role of Exercise in Blood Sugar Control
Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and helps regulate glucose levels. The goal is at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week, such as walking, cycling, or strength training. Even short walks after meals can aid blood sugar regulation.
Step 4: Managing High and Low Blood Sugar
High Blood Sugar (Hyperglycemia)
Symptoms of high blood sugar include fatigue, headaches, blurry vision, and excessive thirst. To bring levels down, drink plenty of water, engage in physical activity, and take any prescribed medications as directed.
Low Blood Sugar (Hypoglycemia)
Signs of low blood sugar include shakiness, sweating, confusion, and an urgent feeling of hunger. The 15-15 Rule is an effective way to address it—consume 15 grams of fast-acting carbohydrates, such as glucose tablets or juice, wait 15 minutes, and then check your levels again.
Final Thoughts: Take Control of Your Blood Sugar
Blood sugar management is a daily balancing act, but small, consistent efforts lead to long-term success. By tracking your levels, making smart food choices, staying active, and working with your healthcare provider, you can take charge of your health and keep your glucose levels in check.